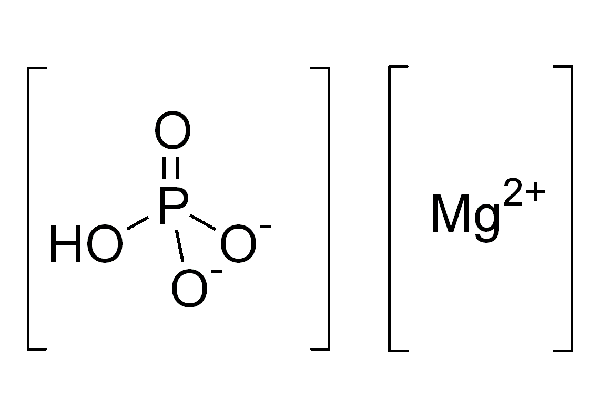
MgHPO₄, a chemical compound often encountered in chemistry, especially in inorganic chemistry, is known by the name Magnesium Hydrogen Phosphate. Understanding the composition, properties, and uses of Magnesium Hydrogen Phosphate requires a closer look at the chemical elements that form it, its molecular structure, and its relevance in various fields.
Understanding the Components of MgHPO₄
To comprehend the naming of MgHPO₄, it’s essential to break down its chemical formula and understand the components:
- Mg: This is the chemical symbol for Magnesium, a metallic element that is essential for many biological processes and widely used in various industrial applications. It is an alkaline earth metal, located in Group 2 of the periodic table, with an atomic number of 12.
- H: This stands for Hydrogen, the lightest and most abundant element in the universe. It is often found in combination with other elements and is a fundamental building block of life.
- PO₄: This represents the phosphate ion, a polyatomic ion consisting of one phosphorus atom covalently bonded to four oxygen atoms. The overall charge of a phosphate ion (PO₄³⁻) is -3, but in the compound MgHPO₄, the presence of hydrogen alters the ion to a hydrogen phosphate ion (HPO₄²⁻) with a charge of -2.
When these components come together to form MgHPO₄, the compound is named Magnesium Hydrogen Phosphate, indicating the presence of magnesium and hydrogen phosphate ions.
The Naming of Magnesium Hydrogen Phosphate
In chemical nomenclature, the name of a compound typically reflects the elements and their proportions within it. The name Magnesium Hydrogen Phosphate indicates the presence of magnesium (Mg), hydrogen (H), and phosphate (PO₄) in the compound. Here’s a breakdown of the naming convention:
- Magnesium (Mg): This comes first in the name as it is the metal cation with a +2 charge.
- Hydrogen Phosphate (HPO₄²⁻): This comes second and represents the anion composed of hydrogen and phosphate. The hydrogen in this context is not a free element but part of the hydrogen phosphate ion, which is different from a phosphate ion by the presence of one additional hydrogen atom, reducing the overall negative charge from -3 to -2.
By following these naming conventions, the compound MgHPO₄ is accurately named Magnesium Hydrogen Phosphate.
Properties of Magnesium Hydrogen Phosphate
Magnesium Hydrogen Phosphate has several notable properties that make it useful in various applications:
- Solubility: Magnesium Hydrogen Phosphate is moderately soluble in water. Its solubility is dependent on the pH of the solution, becoming more soluble in acidic conditions. This property is significant when considering its use in agricultural and medical applications where pH levels can vary.
- Crystal Structure: This compound typically forms as a crystalline solid. The crystal structure can vary depending on the conditions under which it is synthesized, but it generally adopts a structure that allows for the stabilization of the hydrogen phosphate ion and magnesium.
- Stability: Magnesium Hydrogen Phosphate is stable under normal conditions but can decompose when heated to high temperatures, breaking down into magnesium pyrophosphate and water.
Uses and Applications of Magnesium Hydrogen Phosphate
Magnesium Hydrogen Phosphate has several important applications across different fields due to its chemical properties:
- Agriculture: In agriculture, Magnesium Hydrogen Phosphate is used as a fertilizer. Phosphates are essential nutrients for plants, promoting root development and flowering. The magnesium component is also beneficial as it is a critical element in chlorophyll, aiding in photosynthesis and overall plant health.
- Medical and Pharmaceutical: In the medical field, Magnesium Hydrogen Phosphate is sometimes used as a dietary supplement to address deficiencies in magnesium and phosphorus. Magnesium is crucial for various bodily functions, including muscle and nerve function, blood sugar control, and blood pressure regulation. Phosphates are essential for bone and teeth formation, as well as energy production.
- Food Industry: It is used as an additive in the food industry, often serving as a leavening agent in baking. It can also act as an acidity regulator and a mineral supplement in various food products.
- Water Treatment: Magnesium Hydrogen Phosphate can be utilized in water treatment processes, particularly in the removal of heavy metals and other contaminants. The compound can aid in the precipitation of unwanted ions, helping to purify water.
Conclusion
Magnesium Hydrogen Phosphate (MgHPO₄) is a versatile compound with a wide range of applications in agriculture, medicine, food, and water treatment. Understanding its composition, properties, and uses highlights the importance of this compound in both industrial and everyday contexts.
By breaking down the name and components of MgHPO₄, we see how the nomenclature reflects the elements present and their respective charges. This clarity in naming is crucial for the proper identification and application of chemical compounds in various fields, ensuring that Magnesium Hydrogen Phosphate is correctly utilized to benefit multiple industries and consumers alike.
Post time: Aug-29-2024